

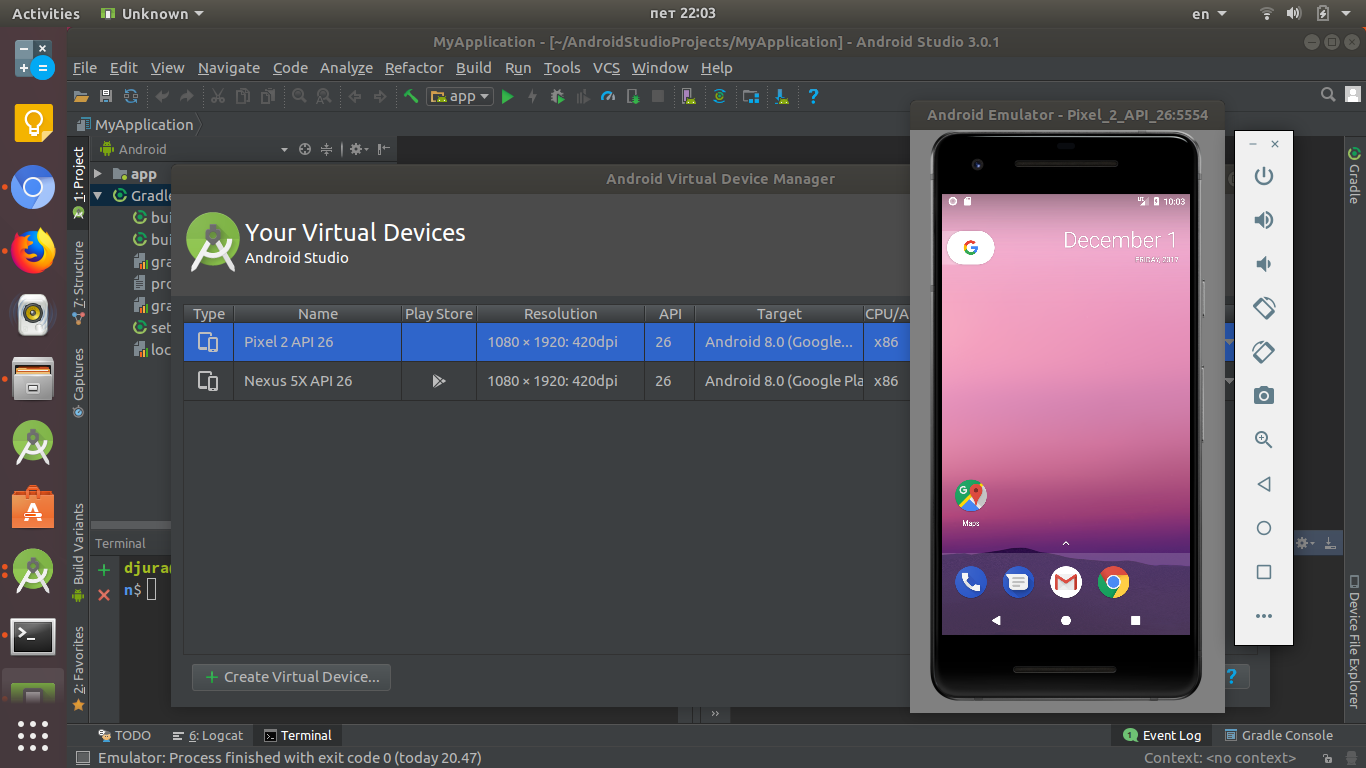
(Clear any checkboxes that were auto-selected.) In the packages tree, locate and check the ARM EABI v7a System Image node within the first Android node in the list.įor example: Android 4.2.2 (API 17) or Android 4.3 (API 18).Start the Android SDK Manager (select Start | All Programs | Embarcadero RAD Studio | Android Tools).In this case, you do not need to install another Android system image. Note: If you installed the Android SDK and NDK during RAD Studio installation, a valid Android system image (such as Android 4.2.2 API 17) should already be shown as Installed in the Android SDK Manager. Installing an Android System Image (Required)īefore you create an Android emulator, you need to install an Android system image that your emulators can use. The installed Android emulator is named rsxe5_android, which uses the WVGA800 skin and Android 4.2.2. It is a well-known performance issue that Android emulators are extremely slow.Although an emulator might run on a VM, the emulator will not run an application. You cannot use an Android emulator on a Virtual Machine (VM).
Android devices that are ARM version 7 or newer.Android emulators that are version 4.0 or newer.RAD Studio supports the following targets:.
If you create your own Android emulator, consider creating an emulator for each Android device you want to support.This emulator is used as the default target for an Android application, so you can easily create and run an Android application on your development system.We recommend that you install this emulator during product installation.An Android emulator is installed by default during the RAD Studio installation.

You can use an Android emulator as a target platform to run and test your Android applications on your PC. An Android emulator is an Android Virtual Device (AVD) that represents a specific Android device.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
